What is cardiac arrest step 2
Cardiac arrest step 2 looks at the practical application of Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR). The cardio (cardiac compressions) phase refers to when you compress the chest. The pulmonary section is the rescue breathing phase. Explicitly the 2 are combined generally. Henceforth oxygenation occurs likewise. There are various versions of CPR in cardiac arrest step 2. These variations depend upon the cause and age of the patient obviously.
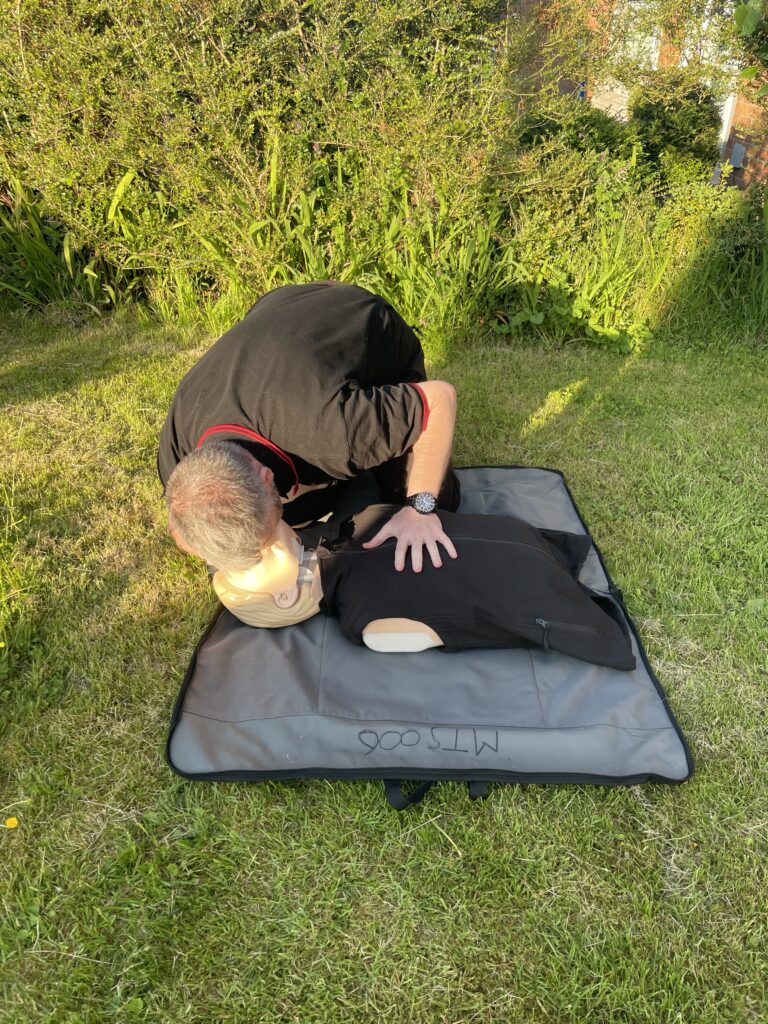
Cardiac arrest step 2 cardiac compressions
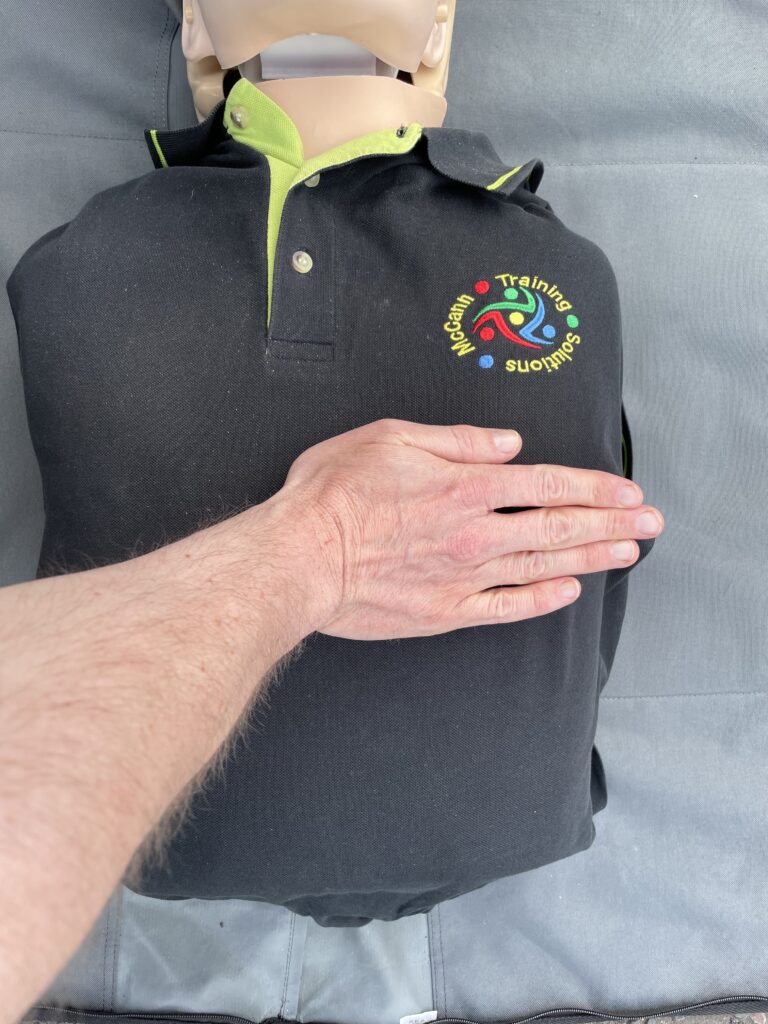
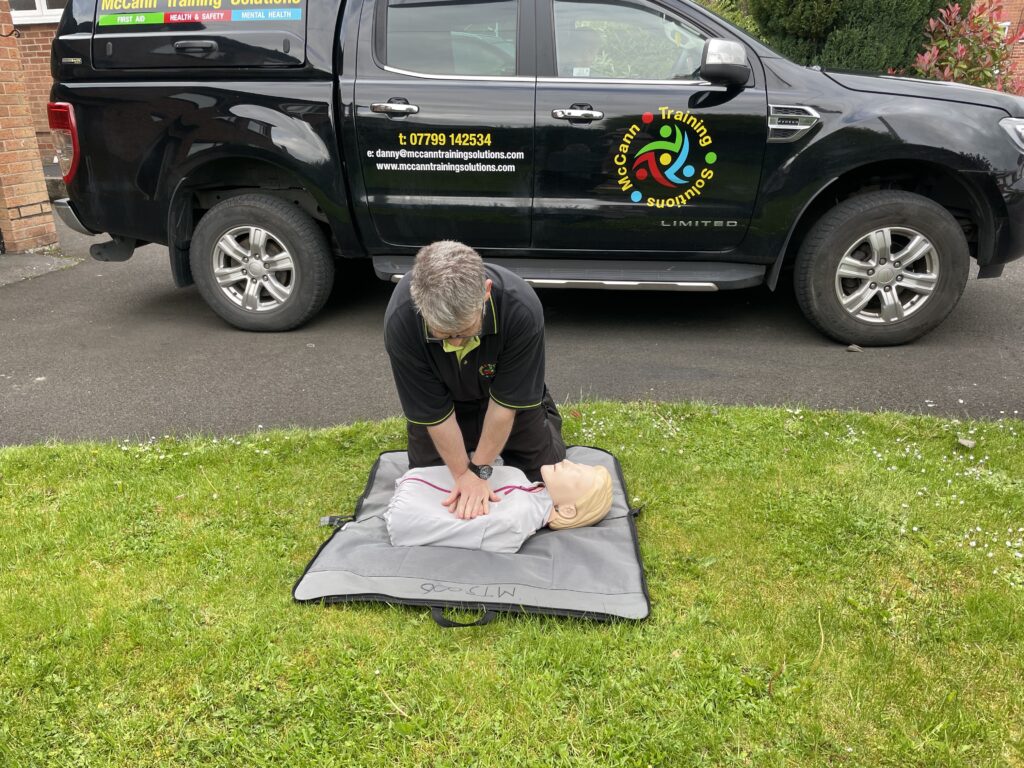
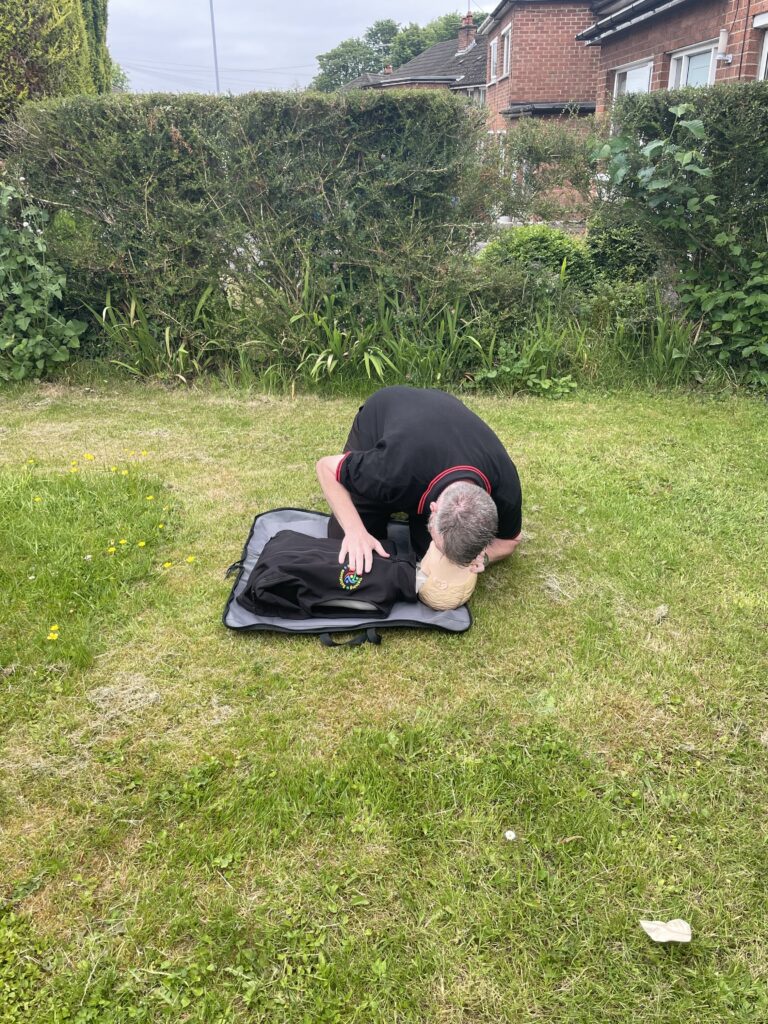
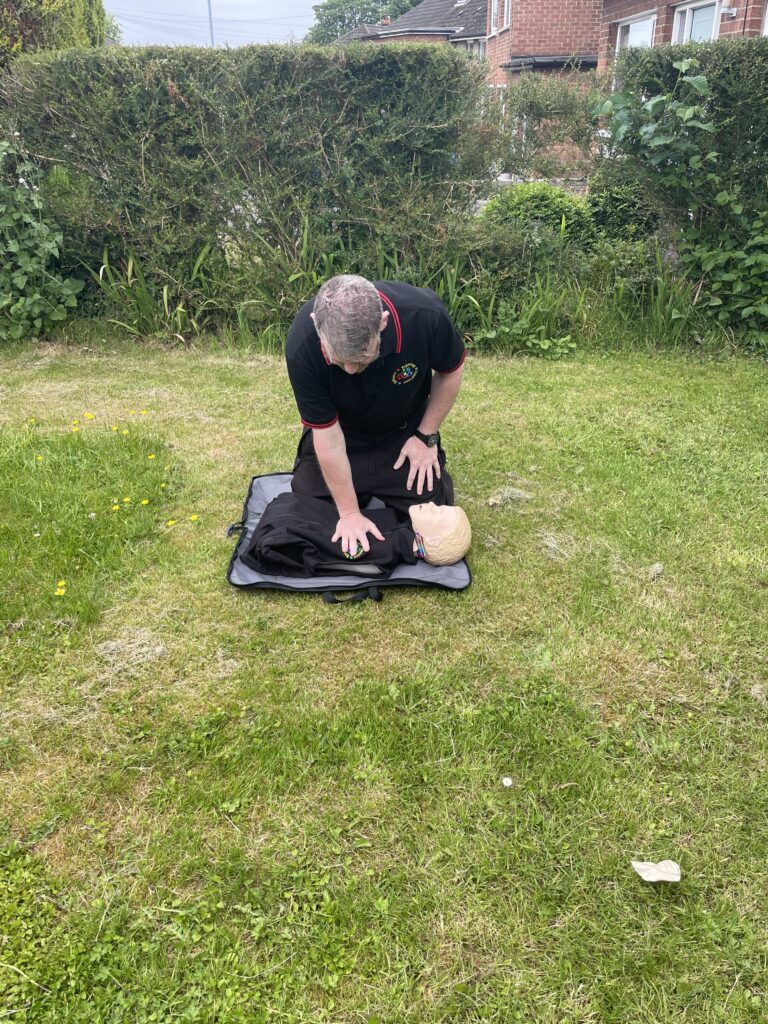
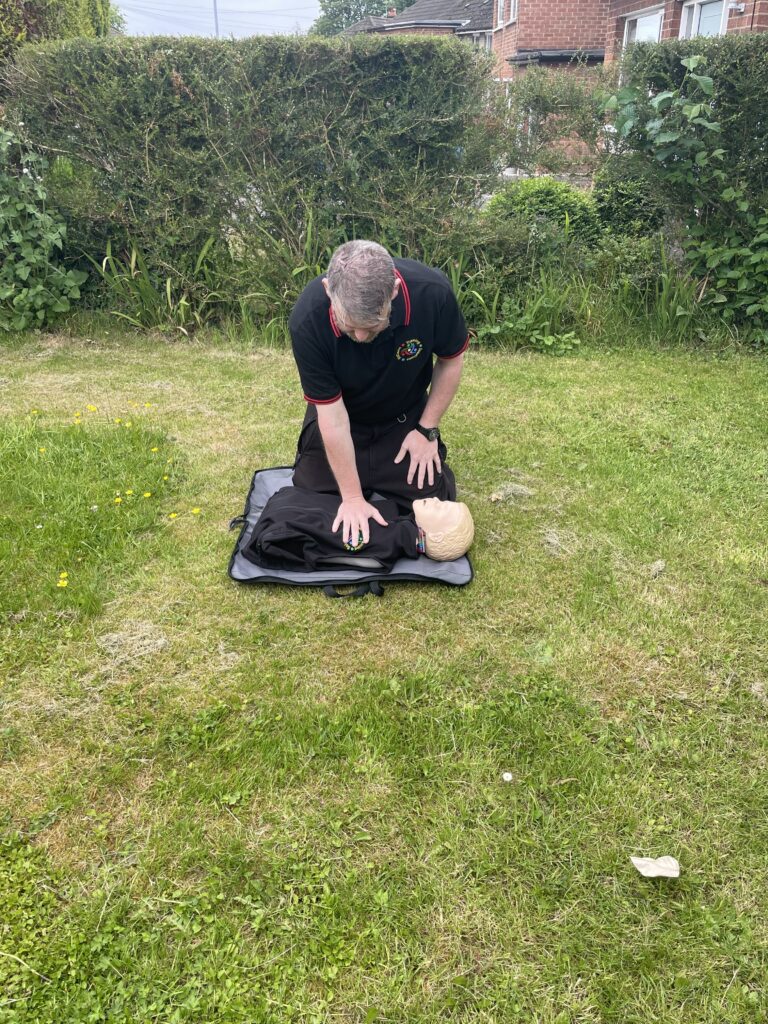
There are 3 different stages in cardiac compressions besides. Stage 1 has the heel of one hand placed on the centre of th chest. During stage 2, the second hand is placed on top of the first. Stage 3 has your knees centralised on the patients chest with your core engaged. The chest is then compressed downwards approximately 5-6 cm. The compression is then released to allow full expansion of the chest again.
If you’re dealing with an adult from non drowning incident. 30 compressions are administered by placing both hands on the centre of the chest. The chest is compressed down approximately one third the depth. This is roughy 5-6 centimetres. If it is a paediatric use 1 hand instead of both. Compress again around 1/3 the depth of the body. Infants (under one) use 2 fingers in the centre of the chest. Infants must be resuscitated on a soft surface. Cardiac compressions can be conducted on their own. This is known as hands only CPR especially . The delivery rate is 100-120 compressions a minute

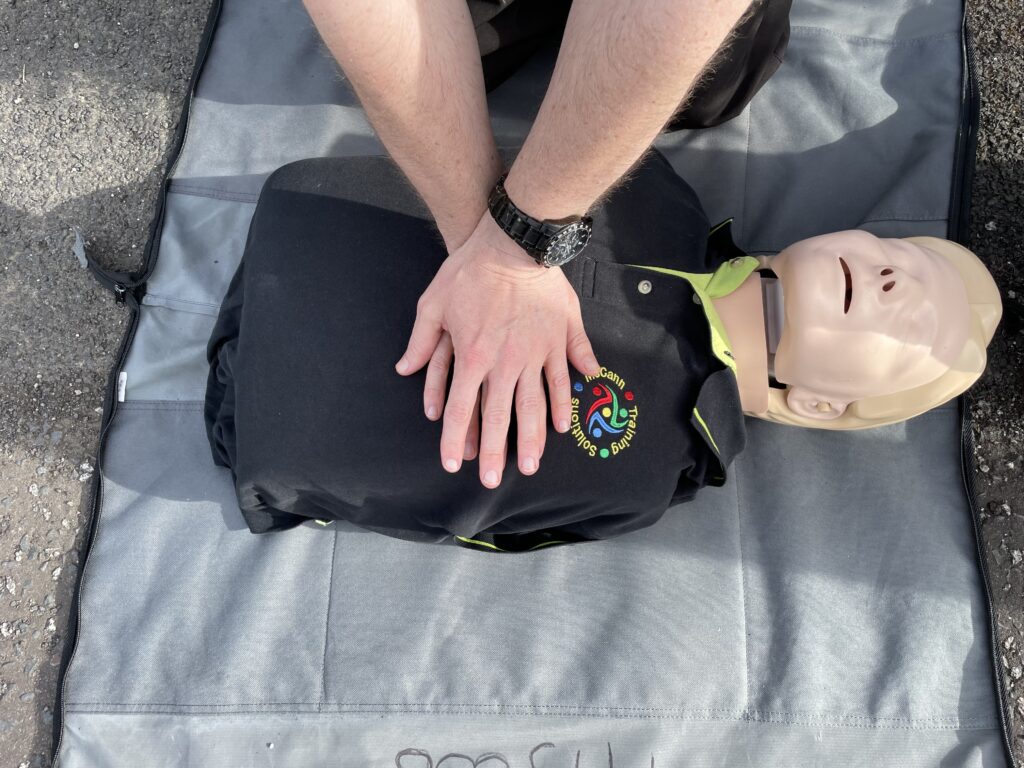

Cardiac arrest step 2 rescue breathing
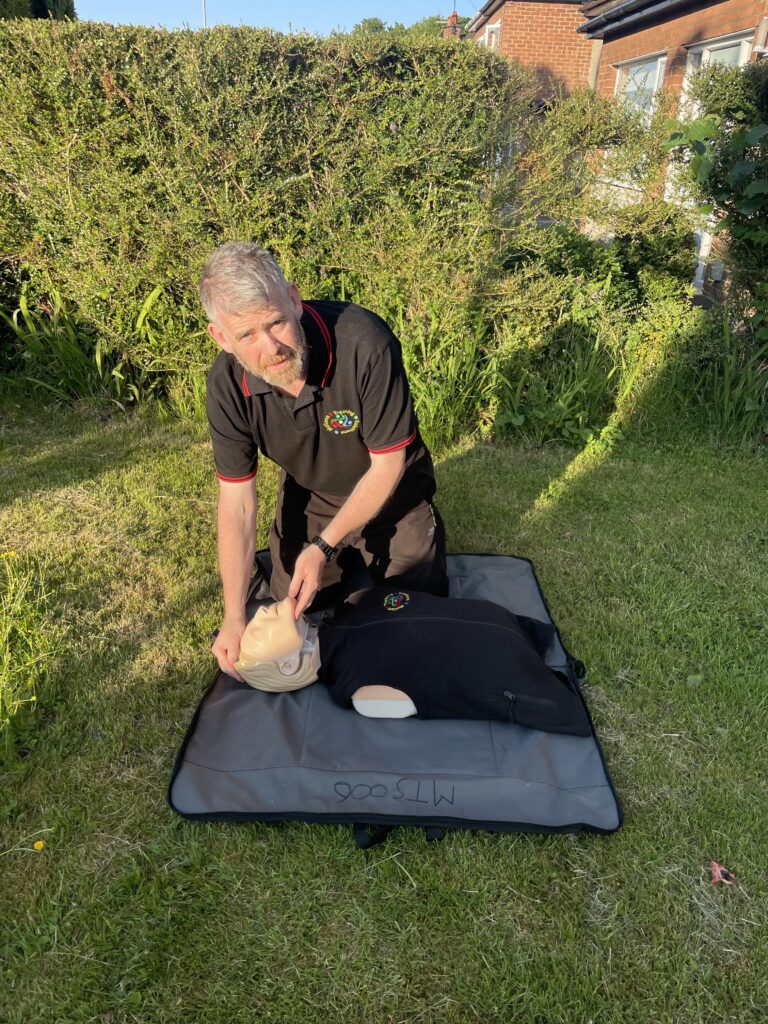
Nonetheless rescue breathing however is delivered to increase oxygen levels in the lungs. In adults 2 rescue breaths are delivered correspondingly after every 30 compressions. Pinching the patients nose shut firmly. Tilt the head back and lift the chin. Place one hand on the patients chest. seal your lips around theirs. Blow in once allowing your hand to rise and fall on the chest. Evidently take in breath yourself and repeat a second time comparatively.

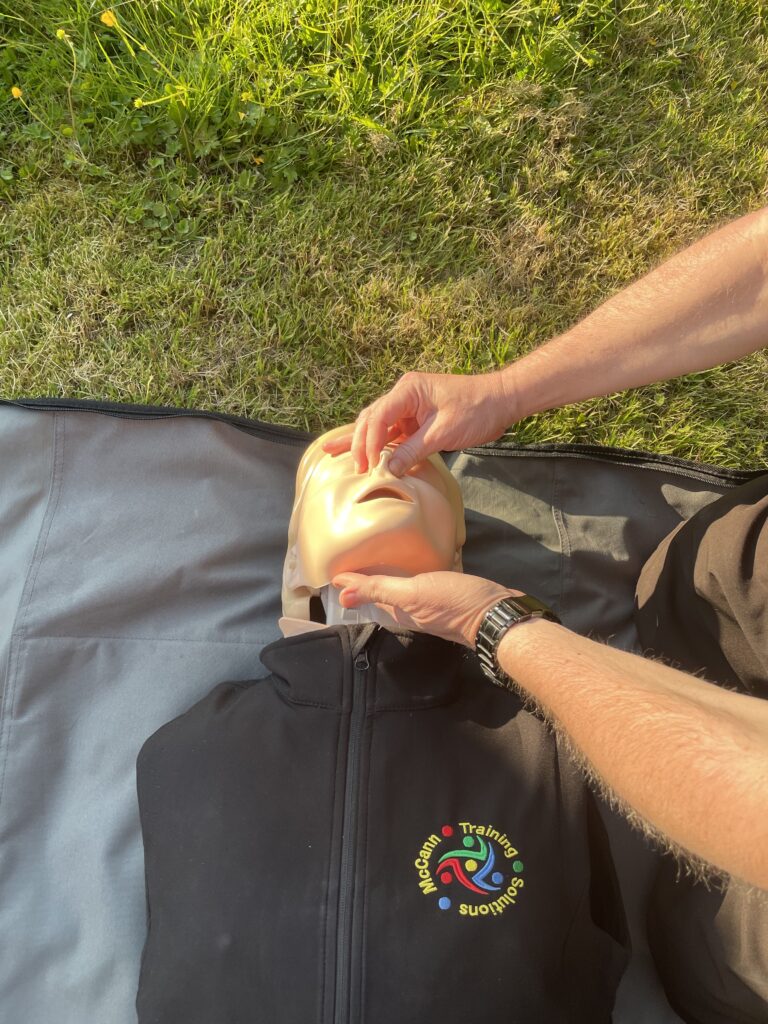

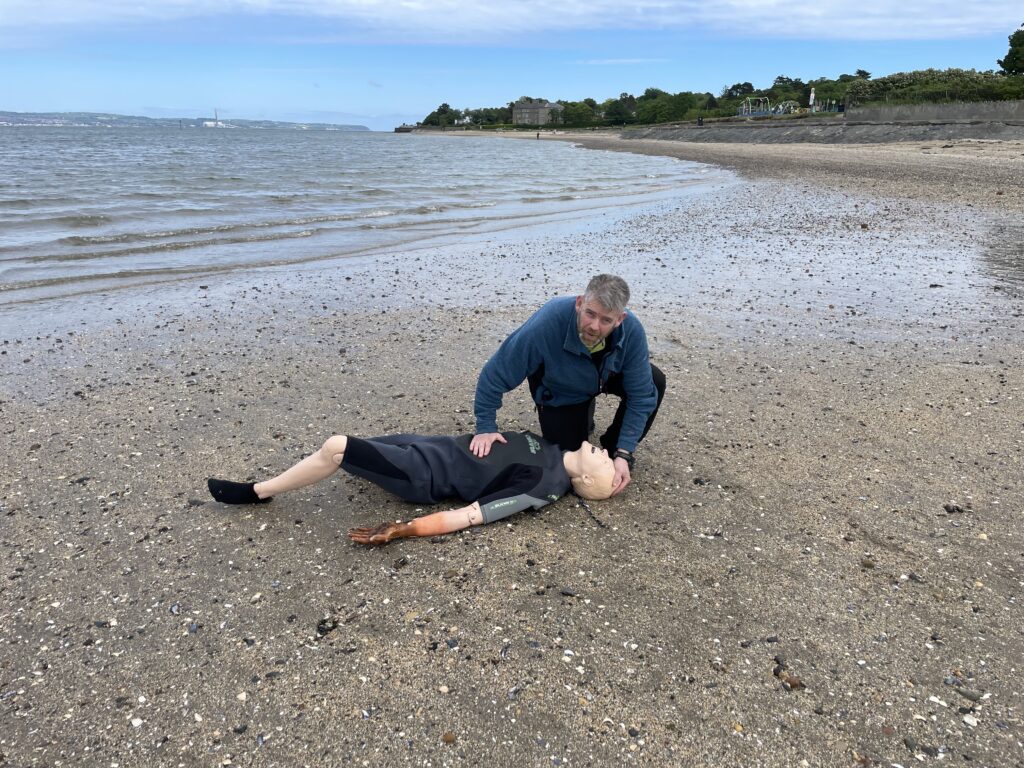
Drowning CPR
Drowning CPR takes a different stance. 5 rescue breaths are delivered on a hard surface moreover stability. Otherwise 30 compressions then 2 rescue breaths shortly. drowning victims must be taken to hospital. This is to check for secondary or dry drowning. This is where the lungs can fill up again.
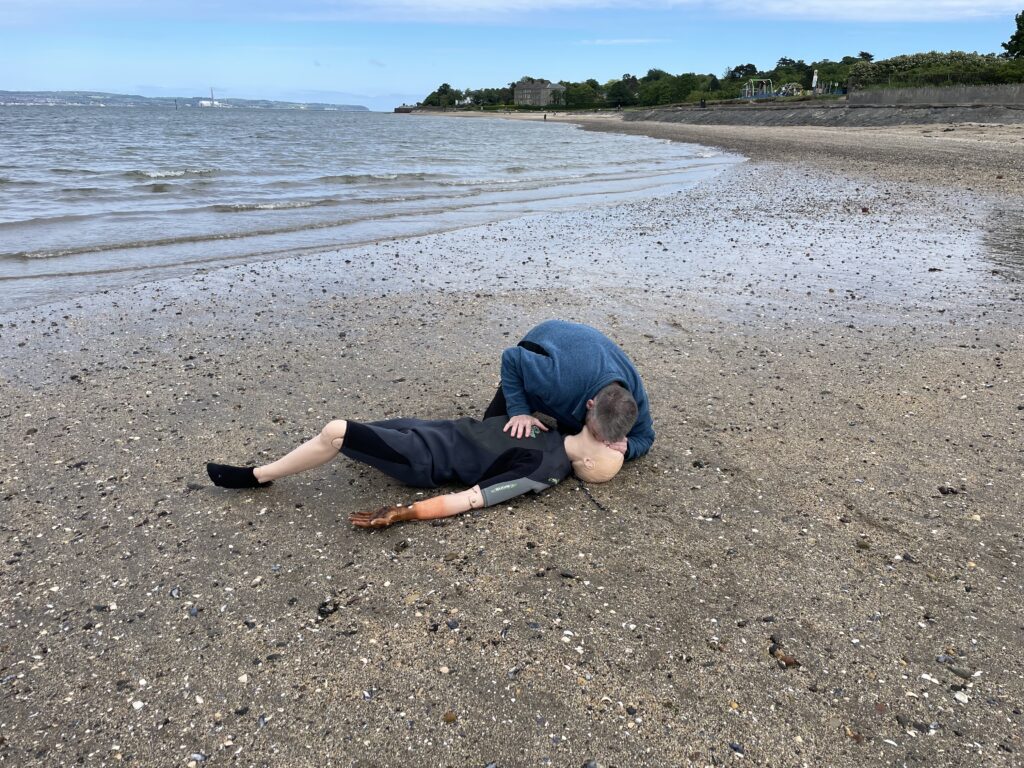
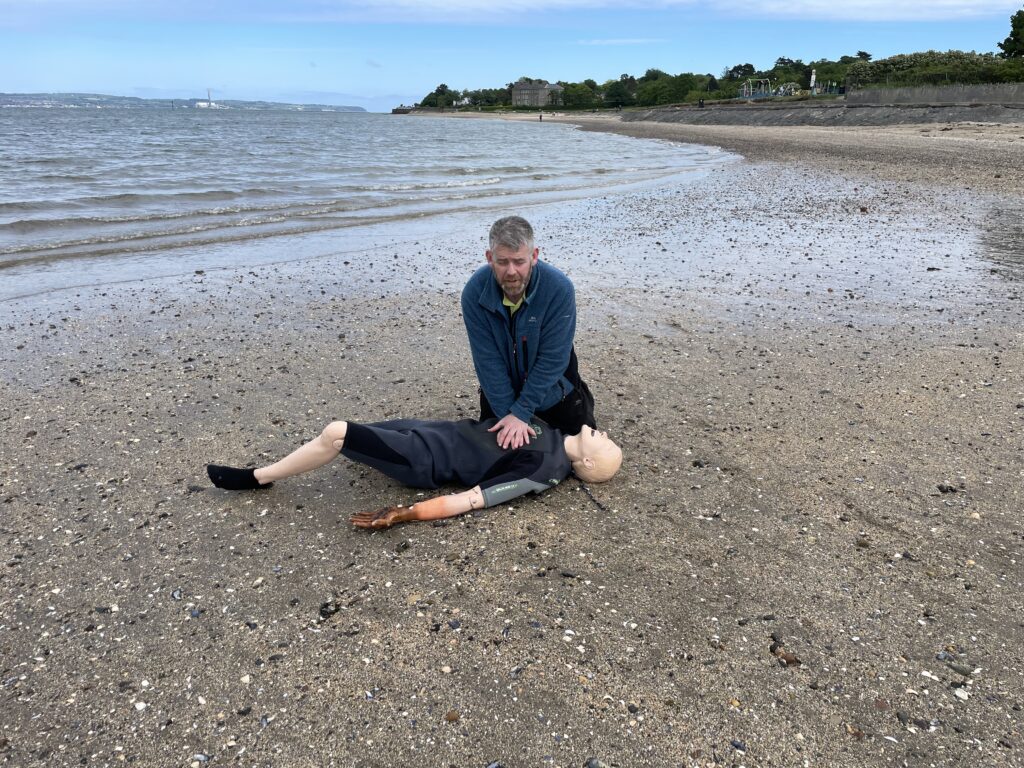



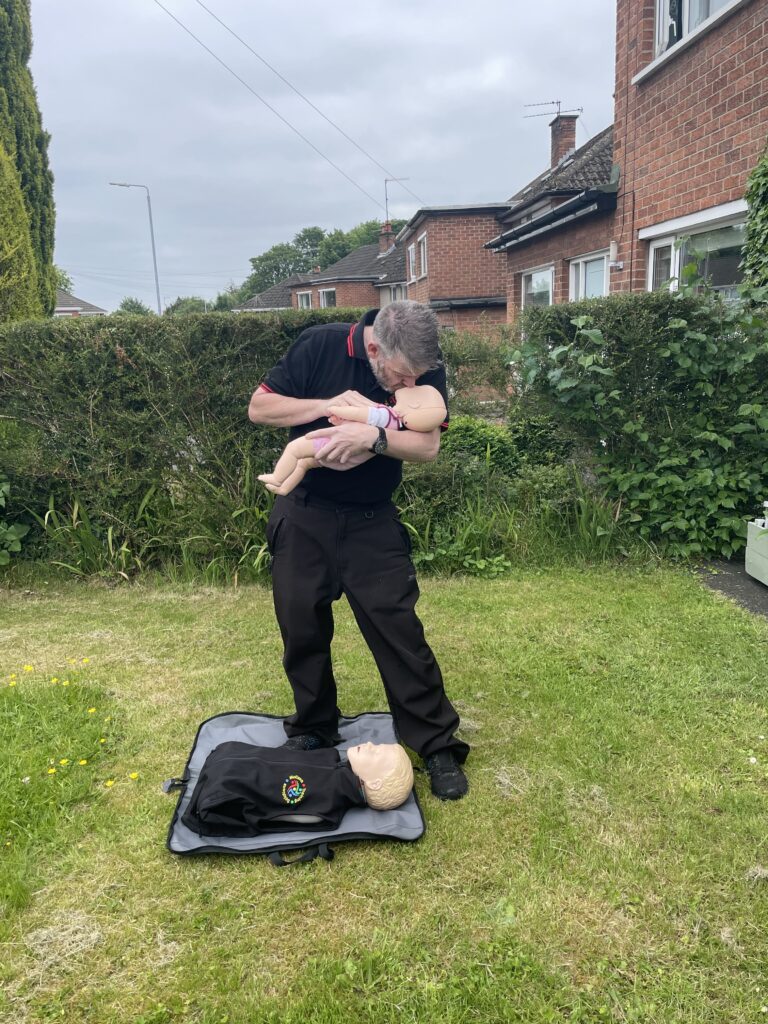
Paediatric or infant CPR
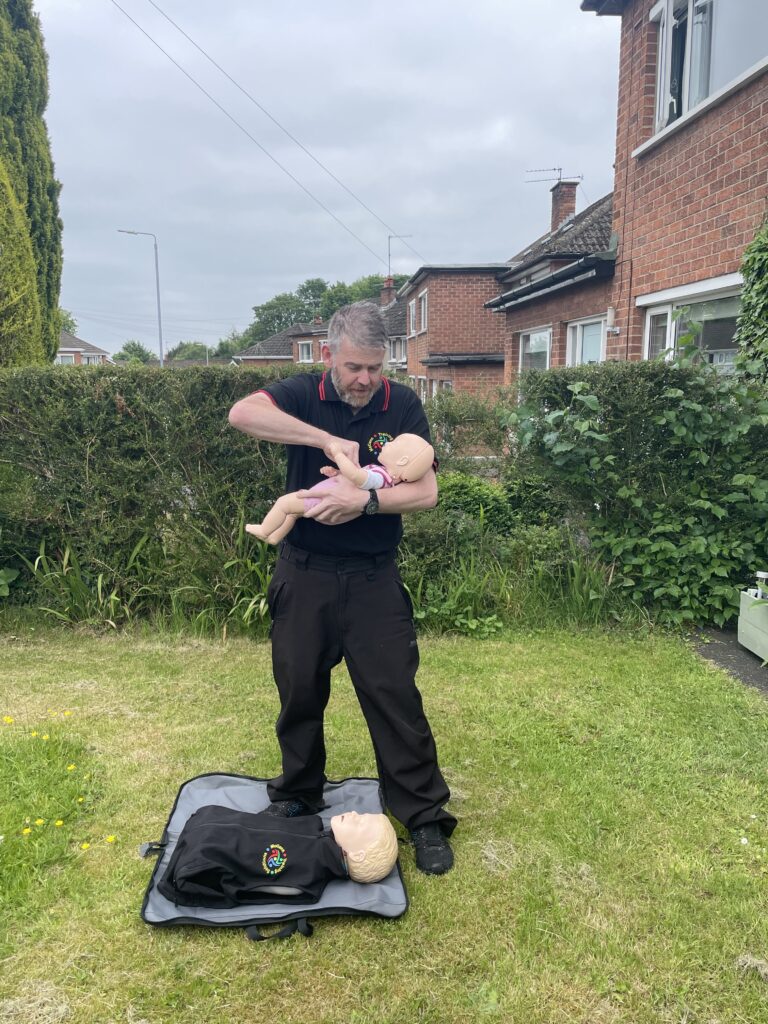
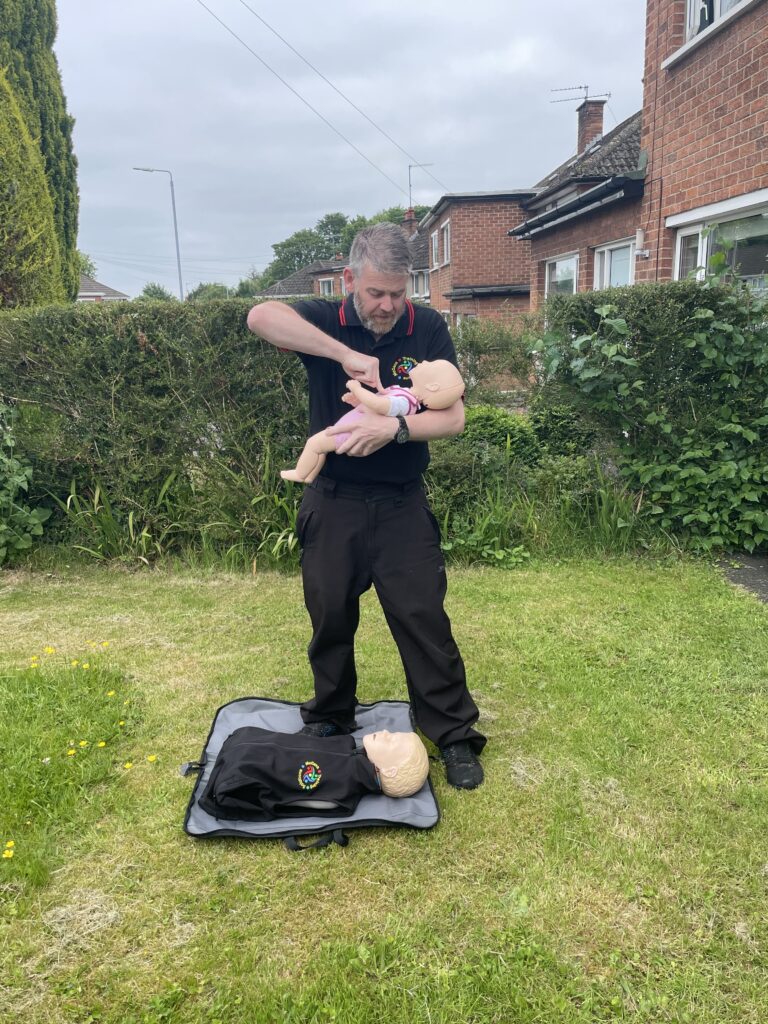
Paediatric or infant CPR has the same approach as drowning subsequently. 5 rescue breaths are delivered. Afterward the regime of 30 compressions and 2 breaths takes over. Paediatrics are aged between 1-18. One hand is used on compressions altogether another aspect is your strength. With lungs being smaller basically the breath input is smaller. However if needs must use a second hand to achieve an effective compression. Infants are under the age of 1. Basically the same regime is observed. However two fingers are used for compressions. Rescue breathing is achieved by sealing the infant’s mouth and nose. This is because of anatomical positions. Despite sixe oxygen is required quickly.




Steps to cardiac arrest
There are 4 steps to cardiac arrest. Learn more about cardiac arrest and the causes
- Step 1 – Early recognition of cardiac arrest and call for professional help
- Step 2 – Early CPR must be initiated
- Step 3 – Early access to defibrillation is critical likewise and combined with CPR
- Step 4 Early post resuscitation care to restore the quality of life however also apply.
You can’t change what happens, you change what you do about it
Danny McCann – mccann training solutions